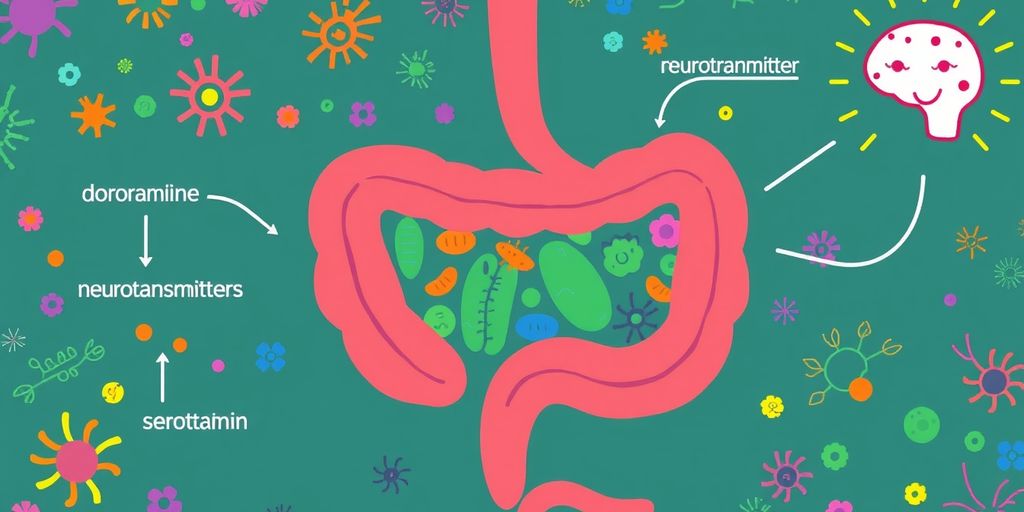
Did you know that your gut can affect your mood? That’s right! The trillions of bacteria living in your digestive system, known as the gut microbiome, play a big role in how you feel. These tiny organisms help produce important chemicals like dopamine, serotonin, oxytocin, and endorphins. These chemicals, often called neurotransmitters, are crucial for mood regulation. In this article, we will explore how these neurotransmitters work and how you can support your gut for better mental health.
Key Takeaways
- Your gut microbiome is closely linked to your mood and mental health.
- Dopamine, produced in the gut, plays a key role in motivation and pleasure.
- Serotonin, mostly made in the gut, helps stabilize your mood and reduce anxiety.
- Oxytocin, influenced by gut bacteria, is important for social bonding and relationships.
- Endorphins, which help manage pain and stress, are also connected to gut health.
The Role of the Gut Microbiome in Mood Regulation
How Gut Bacteria Influence Neurotransmitter Production
The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in producing neurotransmitters like dopamine, serotonin, and others. These chemicals are essential for emotional regulation and cognitive function. Gut bacteria can produce or influence the production of these neurotransmitters, impacting our mood and mental health.
The Gut-Brain Axis: A Two-Way Street
The gut-brain axis is a complex communication network between the gut and the brain. This bidirectional system means that not only does the brain affect gut health, but the gut also influences brain function. Changes in the microbiome can lead to alterations in mood and behavior, highlighting the importance of maintaining a healthy gut.
Impact of Dysbiosis on Mental Health
Dysbiosis, or an imbalance in gut bacteria, can have significant effects on mental health. It has been linked to conditions like anxiety and depression. By understanding and managing dysbiosis, we can potentially improve mental well-being and overall health.
The gut-brain axis is a vital link in understanding how our gut health affects our mental state. Keeping this connection in balance is key to emotional and cognitive well-being.
Dopamine: The Motivational Molecule
Dopamine Production in the Gut
Did you know that about 50% of your dopamine is made in your gut? This important neurotransmitter is not just produced in the brain. Early studies in animals suggest that the microbiome might play a role in this process. This connection was first noticed in research on Parkinson’s disease, a condition linked to problems with dopamine transmission.
Dopamine’s Role in Reward and Pleasure
Dopamine is often called the ‘motivation molecule‘ because it plays a key role in the brain’s reward system. This system controls motivation, desire, and cravings. When you do something enjoyable, like eating your favorite food or winning a game, your brain releases dopamine, making you feel happy and motivated.
Dopamine and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Research shows that changes in the gut microbiome can affect the brain, especially in areas where dopamine-dependent neurons are found. This is important for understanding diseases like Parkinson’s, which are linked to dopamine problems. Taking care of your gut health might help protect your brain and keep you feeling good.
The gut microbiome is like a second brain, producing chemicals that make you happy and healthy.
Serotonin: The Mood Stabilizer
Serotonin Production and the Gut
Serotonin, often called the "feel-good chemical," is mainly produced in the gut. In fact, up to 90% of the body’s serotonin is made there. This neurotransmitter plays a crucial role in regulating mood, digestion, and sleep. Gut bacteria can influence serotonin production, highlighting the importance of a healthy gut for mental well-being.
How Serotonin Affects Mood and Anxiety
Serotonin is essential for stabilizing mood and reducing feelings of anxiety and depression. Low levels of serotonin are linked to mood disorders. This chemical helps you feel calmer, happier, and more focused. When serotonin levels are balanced, it can also help manage the body’s stress response.
Dietary Influences on Serotonin Levels
Your diet can significantly impact serotonin levels. Foods rich in tryptophan, an amino acid, are essential for serotonin production. Examples include turkey, eggs, and nuts. Maintaining a balanced diet can help keep serotonin levels stable, supporting overall mental health.
A healthy gut is crucial for maintaining optimal serotonin levels, which in turn supports a stable mood and reduces anxiety.
Oxytocin: The Bonding Hormone
Oxytocin’s Role in Social Interactions
Oxytocin is a neurochemical that helps humans form social bonds. It makes us feel empathy and brings us closer to others. This hormone is especially high in pregnant women during and after labor. However, it can also create negative memories if the social experience is bad.
Gut Microbes and Oxytocin Production
Gut bacteria can boost oxytocin production. This helps with wound healing and muscle health. Some studies even suggest that this might help people live longer. For example, the probiotic bacteria L. reuteri can increase the body’s natural production of oxytocin.
Natural Ways to Boost Oxytocin
You can increase oxytocin naturally by:
- Spending time with loved ones
- Engaging in caring relationships
- Enjoying soft, friendly touch
- Playing with pets
Although there is an oxytocin supplement, it’s mainly used for childbirth issues and research. Always talk to your doctor before taking any supplement.
Endorphins: The Natural Painkillers
Endorphin Release and Physical Activity
Endorphins are often called nature’s morphine because they act as natural painkillers. They are released by the brain during activities like exercise, eating, or even laughing. This release can lead to a feeling of euphoria, often referred to as a "runner’s high." Physical activity is one of the best ways to boost endorphin levels.
The Role of Endorphins in Stress and Pain Management
Endorphins help us manage stress and reduce pain. When you experience pain or stress, your brain releases endorphins to help you cope. These chemicals can also help reduce inflammation, making them important for overall health. They are part of the body’s natural response to stress and discomfort.
Gut Health and Endorphin Levels
Your gut health can impact your endorphin levels. A healthy gut microbiome can help regulate the production of these natural painkillers. Eating a balanced diet rich in fiber, fruits, and vegetables can support a healthy gut and, in turn, help maintain optimal endorphin levels.
Keeping your gut healthy can help you manage pain and stress better.
Diet and Lifestyle Choices for a Healthy Microbiome
Foods That Support Neurotransmitter Production
Your diet plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy Microbiome. Eating foods rich in dietary fiber like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help increase bacterial diversity in your gut. Including probiotics such as yogurt, kefir, and fermented foods can also support the growth of beneficial bacteria.
The Impact of Exercise on Gut Health
Regular physical activity is not only good for your body but also for your gut. Exercise has been shown to boost the diversity of your gut microbiome, which is beneficial for overall health. It can also help increase levels of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which are important for mood regulation.
Stress Management and Its Effects on the Microbiome
Managing stress is essential for maintaining a healthy gut. Chronic stress can negatively impact your gut bacteria, leading to a less diverse microbiome. Practices like mindfulness, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can help reduce stress and promote a healthier gut.
Taking care of your gut through diet, exercise, and stress management can significantly improve your mental well-being.
Conclusion
In summary, the connection between our gut microbiome and mood is both fascinating and significant. The gut produces key chemicals like dopamine, serotonin, oxytocin, and endorphins, which play major roles in how we feel. By taking care of our gut health through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and positive social interactions, we can help boost these ‘happy hormones.’ This means that what we eat and how we live can directly influence our mental well-being. So, remember, a happy gut can lead to a happy mind!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the gut microbiome?
The gut microbiome is a collection of trillions of bacteria and other microbes living in your digestive tract. They help with digestion, nutrient absorption, and even influence your mood and immune system.
How does the gut-brain axis work?
The gut-brain axis is a communication network that links your gut and brain. It allows signals to travel back and forth, affecting everything from mood to digestion.
Can gut bacteria really affect my mood?
Yes, gut bacteria can influence your mood by producing neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which are chemicals that help regulate mood and emotions.
What are neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters are chemicals in the brain that transmit signals from one nerve cell to another. They play a key role in shaping everyday life and functions, including mood, sleep, and concentration.
How can I improve my gut health?
You can improve your gut health by eating a balanced diet rich in fiber, exercising regularly, managing stress, and possibly taking probiotics or prebiotics.
What foods help produce serotonin and dopamine?
Foods rich in tryptophan like turkey, eggs, and nuts can help produce serotonin. Foods like bananas, avocados, and dairy products can help boost dopamine levels.